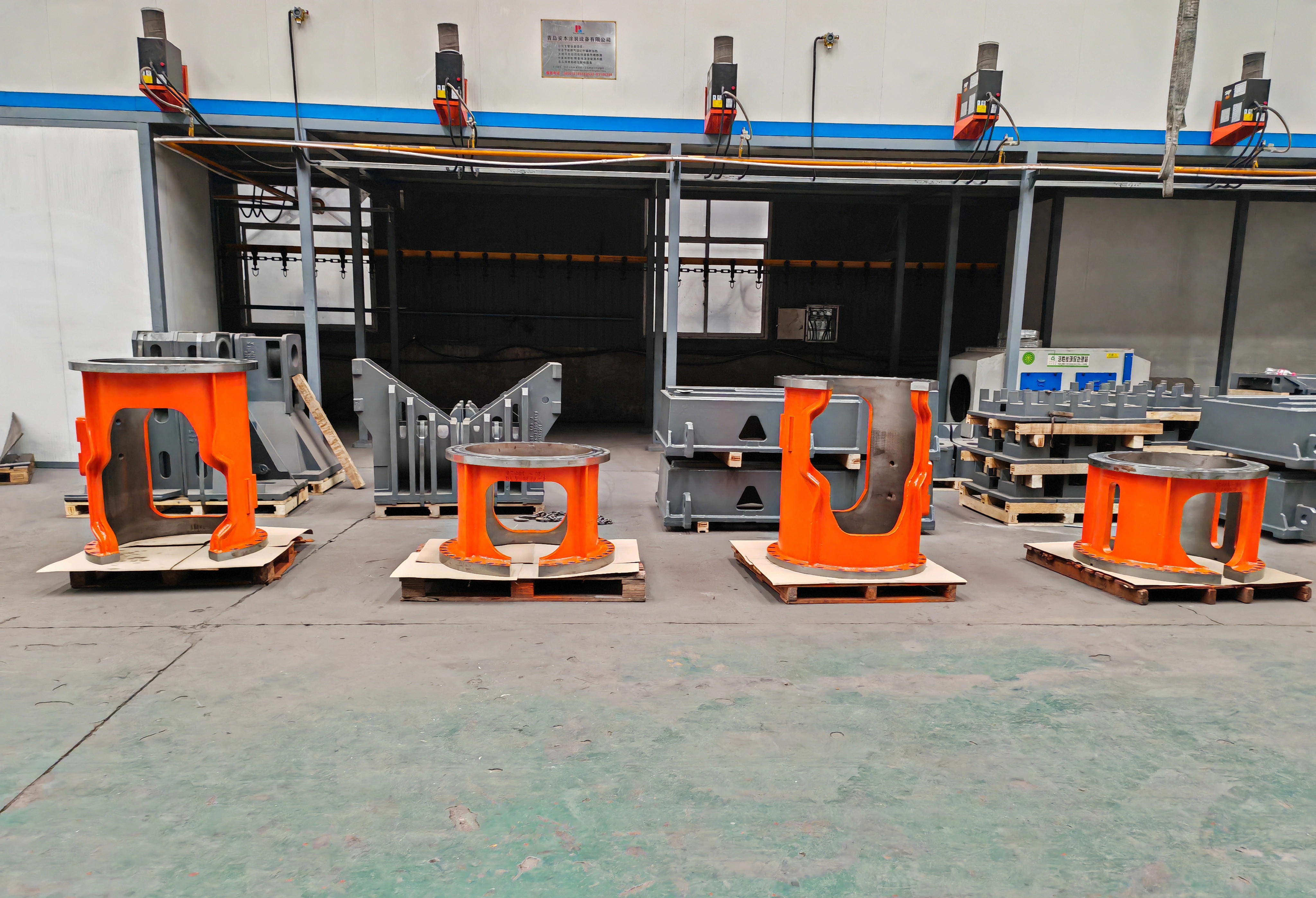
Advantages of White Iron Sand Castings
Exceptional Wear Resistance: The high hardness of white iron, mainly due to the presence of cementite, makes it ideal for parts that experience heavy abrasive wear.
High Hardness: White iron has excellent hardness, making it suitable for components exposed to extreme abrasion, such as crushers and grinding mills.
Cost-Effectiveness: The sand casting process is relatively inexpensive and can be used to produce large quantities of parts, making white iron a cost-effective solution for high-wear applications.
Excellent Surface Finish: White iron castings often have smooth surface finishes, which are beneficial for specific industrial applications.
Types of White Iron
White iron can be modified by adjusting alloying elements to improve certain properties, such as wear resistance, toughness, or corrosion resistance.
1. Standard White Iron:
Pure white iron, with high carbon content (typically 3.5-4.0%) and low silicon. It is extremely hard but brittle.
2. Chromium White Iron:
Chromium is added to increase the hardness and wear resistance of the white iron. It is often used in more demanding abrasive applications. Chromium content typically ranges from 10% to 30%.
Applications: Crushing and grinding machinery, such as crusher hammers, grinding balls, and grinding mill liners.
3. Ni-Hard White Iron:
Nickel is added to enhance toughness without compromising wear resistance. Ni-hard white iron is less brittle than standard white iron and offers good corrosion resistance as well.
Applications: Parts exposed to both wear and corrosion, such as pumps, valves, and marine equipment.
4. Manganese White Iron:
Manganese is added to improve the toughness and impact resistance of white iron, making it less brittle than standard white iron.
Applications: Crusher parts, heavy-duty industrial components, and mining machinery.
Applications of White Iron Sand Castings
White iron sand castings are primarily used in industries where abrasion resistance is the key requirement. The extreme hardness and wear resistance make white iron an ideal material for parts that are exposed to high-stress, abrasive conditions. Below are some common applications:
1. Mining and Mineral Processing
White iron sand castings are widely used in the mining industry for equipment that needs to withstand abrasive wear from materials like coal, ore, and rock.
Crusher Parts: Crusher jaws, mantles, blow bars, and liners are often made from white iron due to its ability to resist wear in high-impact, abrasive environments.
Grinding Mill Liners: Ball mill liners and rod mill liners made from white iron can withstand the continuous impact and abrasive forces in mineral grinding applications.
Chutes and Hoppers: White iron is used for chute liners, hopper liners, and transfer plates to protect against wear caused by the movement of abrasive materials like ores and aggregates.
Benefits in Mining:
Abrasion Resistance: White iron is highly resistant to abrasive wear, making it ideal for mining machinery exposed to crushing, grinding, and other abrasive activities.
High Hardness: The high hardness of white iron ensures long service life in harsh environments.
Cost-Effective: Sand casting is a cost-effective way to produce large quantities of white iron components for the mining industry.
2. Cement Industry
In the cement industry, where equipment is exposed to harsh, abrasive materials, white iron is used for components that need to withstand wear and high temperatures.
Cement Mill Liners: Ball mill liners, grinding media, and shell liners in cement mills are made from white iron to endure the continuous abrasion from the raw materials, including limestone and clinker.
Crusher Liners: Crusher hammers, impact plates, and grinding liners made from white iron are used to break down and process raw materials into cement.
Kiln Parts: Components such as kiln rollers and support bearings are often cast in white iron to endure high temperatures and abrasive wear.
Benefits in Cement:
Wear Resistance: White iron provides excellent protection against the wear from cement and other mineral products.
High Temperature Resistance: White iron’s hardness and resistance to thermal stress are valuable in high-temperature applications such as kilns and crushers.
Extended Component Life: The durability of white iron reduces maintenance costs and downtime in cement plants.
3. Power Generation
In power plants, where equipment is exposed to high temperatures, high pressures, and abrasive environments, white iron sand castings play an important role in protecting vital components.
Coal Pulverizer Parts: Mill liners, grinding balls, and bull rings in coal pulverizers are made from white iron for its wear resistance and ability to withstand the grinding of coal into fine powder.
Ash Handling Components: Ash hoppers, conveyors, and blowers are often made from white iron to handle the abrasive nature of ash in power plants.
Valve Parts: Valve seats, discs, and gate valves in power plants are sometimes cast in white iron to resist erosion caused by high-speed fluids.
Benefits in Power Generation:
Erosion and Abrasion Resistance: White iron components are highly resistant to erosion from fly ash and other abrasive particles in power plants.
Heat Resistance: The ability of white iron to resist wear at high temperatures makes it ideal for power plant applications.
Long Service Life: Components made from white iron last longer in power generation systems, leading to lower operational costs.
4. Steel and Metallurgical Industry
White iron is often used in the steel industry for casting components that are exposed to extreme abrasion, particularly in high-wear areas of steel mills.
Slag Pots: White iron is used in the casting of slag pots, which collect molten slag from the steel production process.
Roller Surfaces: Rolls and grinding rolls used in mills are often made from white iron to withstand abrasive conditions and the crushing of metals.
Casting Machine Components: Casting dies and molds are cast from white iron to handle the wear from molten metal in the production of steel.
Benefits in Steel Industry:
Wear and Abrasion Resistance: White iron provides resistance to the abrasive wear experienced in steel mills.
High Strength: The high hardness and strength of white iron make it suitable for heavy-duty applications in steel production.
Thermal Shock Resistance: White iron can handle the rapid temperature changes encountered in steel manufacturing processes.
5. Industrial Equipment
White iron sand castings are used in various industrial applications, particularly where components are subjected to high wear from abrasive materials or high mechanical forces.
Hydraulic Equipment: Parts such as pump casings, impellers, and valve bodies in hydraulic systems are often cast from white iron for its wear and corrosion resistance.
Heavy-duty Gears: Gear wheels, pinions, and rotors made from white iron are used in equipment like crushers, mills, and industrial machinery where wear resistance is essential.
Transportation Equipment: Components in conveyor systems, rollers, and bearing housings are cast in white iron to reduce wear from the continuous motion of materials.
Benefits in Industrial Equipment:
Abrasion Resistance: White iron excels in applications involving the continuous movement of abrasive materials.
Strength: Its high hardness ensures that components can handle significant mechanical forces without failure.
Reduced Maintenance: White iron’s durability leads to fewer replacements and less downtime, lowering maintenance costs.
6. Marine and Offshore
In the marine industry, where equipment is exposed to both abrasive forces and corrosive seawater environments, white iron is used for components that need to endure extreme conditions.
Marine Pumps: Pump casings, impellers, and pumps for marine applications are often made from white iron for its resistance to wear and corrosion.
Offshore Equipment: Drill bits, valves, and couplings used in offshore oil and gas platforms are sometimes made from white iron to handle the harsh, abrasive conditions.
Propellers and Shafts: White iron is used in certain marine applications for its hardness and wear resistance, although its brittleness makes it less common in critical, impact-prone parts.
Benefits in Marine:
Corrosion and Wear Resistance: White iron’s resistance to both corrosion and abrasive wear makes it suitable for marine environments.
Toughness and Durability: Components made from white iron last longer under harsh operating conditions, reducing downtime.
High Performance: White iron parts maintain their performance over extended periods in demanding offshore conditions.
Conclusion
White iron sand castings provide excellent wear resistance and durability in a range of industrial applications, from mining and cement industries to power generation and steel manufacturing. While its brittleness limits its use in impact-prone environments, white iron is an ideal material for parts exposed to abrasive forces, high temperatures, and corrosive conditions. With various alloy modifications such as chromium or nickel, white iron can be tailored to meet the specific demands of different applications, making it a versatile and cost-effective choice for industries requiring high-performance components.
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi