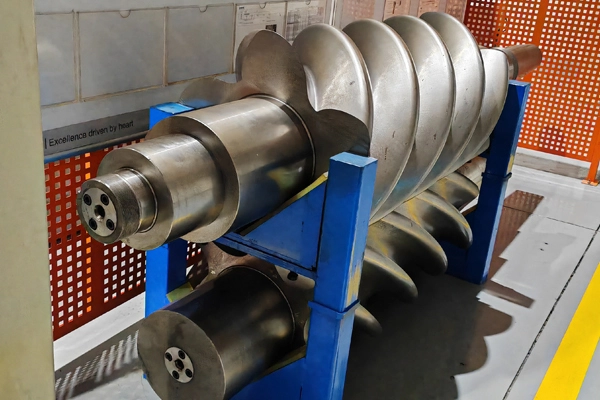
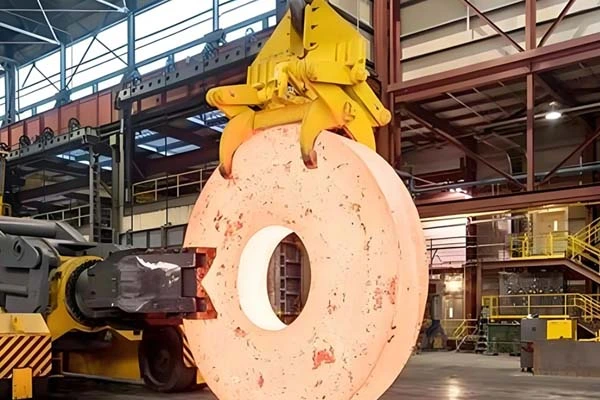
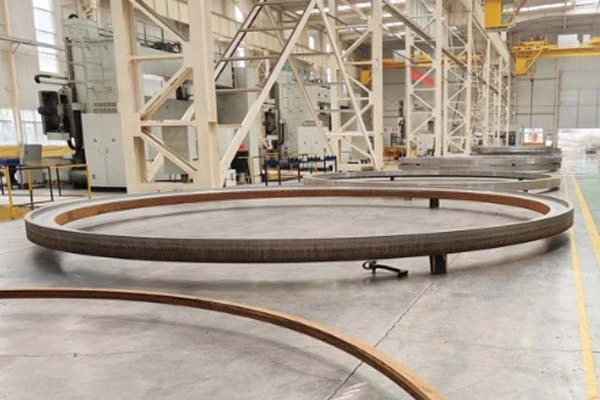
Advantages of Stainless Steel Forging
Superior Strength and Durability: Forged stainless steel components have a superior grain structure, making them stronger and more durable than their cast counterparts.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel alloys, particularly those with high chromium content, are highly resistant to corrosion, oxidation, and staining, making them ideal for harsh environments.
High-Temperature Resistance: Certain grades of stainless steel are designed to withstand high temperatures, making them suitable for high-heat applications.
Excellent Aesthetic Appeal: Stainless steel has a polished, attractive finish, which is important in applications requiring a good appearance.
Customization: The forging process allows for precise control over the final shape, size, and mechanical properties of the part.
Applications of Stainless Steel Forging
1. Automotive Industry
Crankshafts: Stainless steel is used for crankshafts in high-performance engines, offering the necessary strength to withstand high stresses and fatigue.
Transmission Parts: Components like gears, shafts, clutch plates, and differential parts in automotive transmissions are often forged from stainless steel for its strength, wear resistance, and ability to withstand harsh operating conditions.
Suspension Components: Control arms, shock absorbers, steering racks, and axles are forged from stainless steel to ensure strength, impact resistance, and longevity under heavy loads.
Exhaust Systems: Forged stainless steel components like exhaust manifolds and mufflers are used in automotive exhaust systems for their ability to resist corrosion from high-temperature gases.
Benefits in Automotive:
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel's ability to resist rust and corrosion is critical in automotive applications, especially in components exposed to the elements.
Durability and Performance: Forged stainless steel components provide the durability and performance needed in demanding automotive applications.
2. Oil and Gas Industry
Drill Bits and Collars: Forged stainless steel is used to make drill bits, drill collars, and tubular components for oil and gas drilling. The high strength and corrosion resistance are essential for these components to withstand harsh underground environments.
Valve Components: Valve bodies, seats, actuators, and flanges used in oil and gas pipelines and refinery systems are often made from forged stainless steel for its resistance to high pressures, temperatures, and corrosion.
Pump Parts: Stainless steel is used to forge critical pump shafts, impellers, discs, and casing components for pumps in oil and gas operations. These parts need to handle abrasive and corrosive fluids at high pressures.
Wellhead Equipment: Forged stainless steel is used in wellhead equipment, which must be resistant to both high pressure and the corrosive nature of the fluids in the well.
Benefits in Oil and Gas:
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel is crucial in preventing corrosion in harsh environments such as saltwater, acids, and high-pressure fluids.
High-Pressure Resistance: Stainless steel forgings provide the strength needed to endure high-pressure applications like drilling and pipeline systems.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Processing Equipment: Stainless steel is widely used in the food processing industry for equipment such as mixers, blenders, hoppers, and pumps. Stainless steel's non-reactive properties ensure that food products remain uncontaminated by corrosion or rust.
Storage Tanks: Storage tanks and vessels used in the dairy, brewing, and beverage industries are forged from stainless steel to prevent contamination and withstand repeated cleaning processes.
Valves and Fittings: Stainless steel valves, fittings, and piping systems are forged for use in food processing plants due to their resistance to corrosion, ease of cleaning, and durability.
Benefits in Food and Beverage:
Non-Reactive: Stainless steel does not interact with food products, ensuring safety and hygiene.
Easy to Clean: The smooth surface of stainless steel makes it easy to clean and sanitize, which is essential in food processing environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel’s ability to resist corrosion from cleaning agents and acidic foods is essential in food and beverage applications.
4. Marine Industry
Propeller Shafts: Stainless steel is used to forge propeller shafts, which must endure seawater’s corrosive effects while maintaining mechanical strength and integrity under high stresses.
Marine Hardware: Components like hatches, cleats, deck fittings, and anchors are often forged from stainless steel, providing the strength and corrosion resistance needed in marine environments.
Offshore Oil Platform Parts: Stainless steel forgings are used in offshore platform components, including anchors, mooring systems, and pressure vessels, due to their ability to withstand seawater corrosion and high-pressure conditions.
Benefits in Marine:
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel is highly resistant to rust and corrosion from saltwater, making it ideal for marine applications.
Strength and Durability: Stainless steel parts are tough and durable, withstanding the harsh conditions of the marine environment.
5. Power Generation
Turbine and Generator Components: Forged stainless steel is used in turbine blades, generator shafts, and discs for power plants due to its strength and resistance to high temperatures and corrosion.
Heat Exchangers: Components like heat exchanger tubes, plates, and fittings are made from stainless steel to withstand high temperatures and pressure while maintaining corrosion resistance.
Pump Components: Pump shafts, impellers, and casings used in power generation plants are forged from stainless steel for durability and to handle high pressures and temperatures.
Benefits in Power Generation:
Heat Resistance: Stainless steel’s ability to withstand high temperatures makes it ideal for turbine and heat exchanger components.
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel’s resistance to corrosion ensures the longevity and reliability of critical power generation equipment.
6. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Reactor Vessels: Reactor vessels, mixing tanks, and pressure vessels in chemical plants are often forged from stainless steel due to its resistance to corrosion, especially in contact with acids, chemicals, and solvents.
Piping Systems: Forged stainless steel pipes, valves, and fittings are used in chemical and pharmaceutical industries for their ability to withstand corrosive chemicals while maintaining a high level of durability.
Pharmaceutical Equipment: Stainless steel is used to forge components for pharmaceutical processing, including mixers, blenders, filters, and storage containers, ensuring hygiene and resistance to contamination.
Benefits in Chemical and Pharmaceutical:
Corrosion Resistance: Stainless steel’s resistance to aggressive chemicals ensures safety and longevity of equipment in these industries.
Hygienic Properties: Stainless steel’s smooth surface makes it easy to clean and sanitize, a critical factor in pharmaceutical and chemical processing.
Common Grades of Stainless Steel Used in Forging
1. 304 Stainless Steel: The most widely used grade of stainless steel for general-purpose applications. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and is commonly used in the food and beverage industry, automotive, and construction.
2. 316 Stainless Steel: Known for its superior resistance to corrosion, especially against chloride environments. It is commonly used in marine, chemical processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
3. 410 Stainless Steel: A martensitic stainless steel used for parts requiring moderate corrosion resistance and high strength, such as valves and gear shafts.
4. 17-4 PH Stainless Steel: A precipitation-hardening stainless steel that provides high strength and corrosion resistance, used in aerospace and industrial applications.
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi