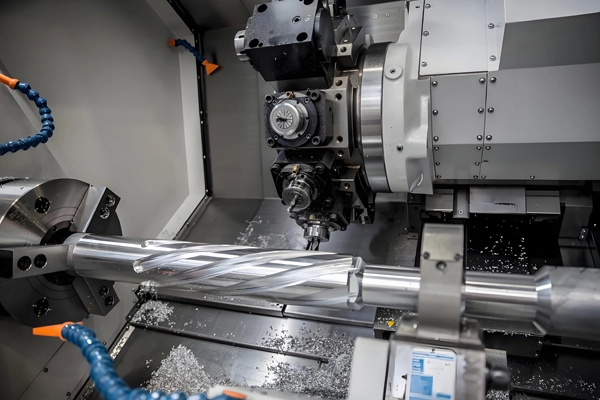
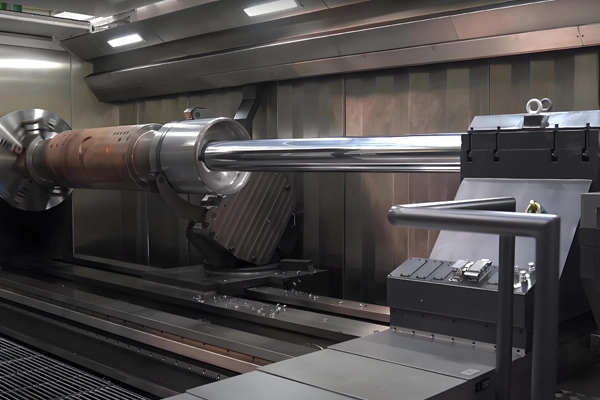
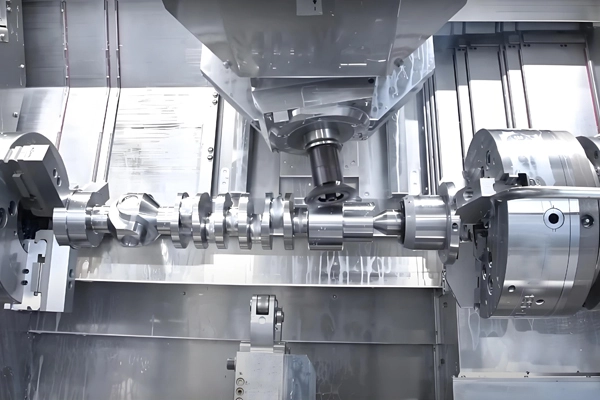
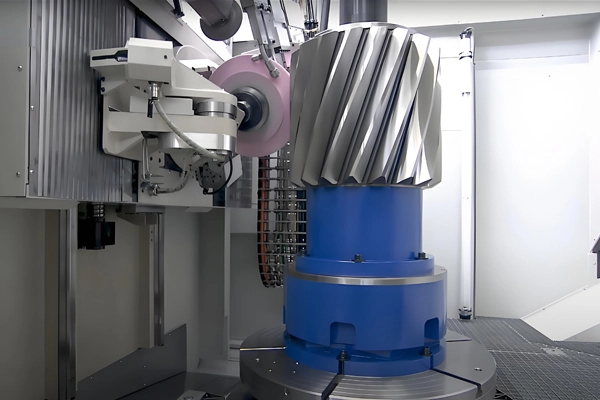
Applications of CNC Profiling and Contouring for Castings and Forgings
1. Complex Shape Creation:
Profiling and contouring are used to create intricate geometric shapes and contours, which are commonly found in automotive engine components, turbine blades, and aerospace parts.
2. Surface Contouring:
3. Forming Critical Geometries:
Parts with complex internal or external profiles, such as irregular cavities, complex grooves, or chamfers, are shaped via profiling and contouring.
4. Mold and Die Manufacturing:
5. Machining of Flanges, Plates, and Frames:
6. Cutting Keyways, Slots, and Holes:
These operations create keyways, slots, and other integral features in forgings or castings, ensuring parts can be assembled or connected properly.
7. Tooling Components:
Recommended Machines for CNC Profiling and Contouring
1. CNC Milling Machines with Profiling Capabilities:
Mazak Variaxis Series: These are high-precision 5-axis machines capable of profiling and contouring complex shapes and 3D surfaces. They are used in high-precision industries like aerospace and automotive.
Haas VF Series: Popular in a range of industries, Haas machines offer a good balance of affordability and capability for profiling and contouring operations.
DMG Mori CMX Series: Known for high-speed and high-accuracy machining, these machines can handle complex profiling tasks, especially for demanding industries like energy and defense.
2. 5-Axis CNC Machines:
Makino a100N: A high-performance 5-axis CNC machine designed for complex contouring and profiling tasks, commonly used for components like turbine blades or intricate aerospace parts.
Hermle C 42 U: An advanced 5-axis machine that allows for high-precision contouring of complex geometries, frequently used for manufacturing molds, tools, and parts with complex curvatures.
3. CNC Vertical Machining Centers (VMCs):
Okuma MB Series: Known for their rigidity and performance, Okuma’s vertical machining centers are ideal for profiling and contouring larger castings and forgings.
Haas VF-4SS: Offers fast spindle speeds and high-precision contouring, ideal for mid-sized castings and forgings in industries like automotive.
4. CNC Lathes with Contouring Capabilities:
Doosan Puma Series: For large castings and forgings that require turning and contouring, Doosan’s CNC lathes provide the necessary flexibility and precision.
CNC Multi-Axis Lathes (e.g., Citizen Cincom): Ideal for contouring complex cylindrical parts, such as valves or housings, with precision threading and profile machining.
5. CNC Water Jet and Laser Machines (for Complex Contouring and Profiling):
Flow International Water Jet Systems: These systems are used for high-precision profiling and contouring of hard-to-machine materials, especially for thin, complex parts with intricate patterns.
Trumpf Laser Machines: High-precision laser cutting systems for contouring metals with tight tolerances and smooth edges.
Dimensional Inspection Measures
1. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM):
CMMs are critical for verifying the dimensions and geometries of profiled and contoured parts. These machines measure the workpiece with probes to check for accuracy in profiles, contours, and geometric features (e.g., angles, radii, and depths).
2. Surface Roughness Testers:
3. Optical Comparators:
4. Laser Scanning Systems:
5. 3D Scanners:
6. Profile Projectors:
7. Micrometers and Vernier Calipers:
Used for quick, manual checks on certain dimensions, such as diameter, depth, and length of specific features.
Inspection Reports
1. First Article Inspection (FAI):
The first part produced from a batch undergoes comprehensive inspection and reports its compliance with all required tolerances, including surface finish, profile, and contour dimensions.
2. Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) Reports:
Reports are provided to document the part’s adherence to geometric tolerances, including position, flatness, roundness, and profile.
3. Surface Finish Reports:
4. Dimensional Inspection Reports:
A detailed report with measurements on critical features such as contour depths, radii, profile angles, and deviations from nominal dimensions.
5. Material Test Reports (MTR):
6. Inspection of Welds or Joints:
Quality Control Measures
1. Pre-Machining Inspection:
2. Tool and Machine Calibration:
3. In-Process Monitoring:
During profiling and contouring, parameters such as feed rate, cutting speed, and tool condition are monitored continuously to ensure consistency and accuracy.
4. Post-Machining Inspection:
After profiling and contouring, parts undergo comprehensive checks for dimensional accuracy, profile smoothness, and conformity to design specifications.
5. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Techniques such as ultrasonic testing, dye penetrant testing, or eddy current testing are used to detect hidden flaws or cracks, especially in critical areas like turbine blades or structural components.
6. Adherence to International Standards:
CNC profiling and contouring processes comply with industry standards such as ISO 9001, AS9100, and IATF 16949, ensuring that all products meet stringent quality and performance criteria.
7. Traceability:
Every part produced is tracked from raw material to final inspection, ensuring that all machining parameters, material certificates, and inspection results are fully traceable.
Advantages of CNC Profiling and Contouring for Castings and Forgings
1. Precision and Accuracy:
CNC profiling and contouring provide high precision, making it possible to create complex geometries and achieve tight tolerances that are critical in industries like aerospace, automotive, and energy.
2. Complex Geometries:
3. Improved Surface Finish:
4. Cost Efficiency for Complex Parts:
5. Consistency:
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi