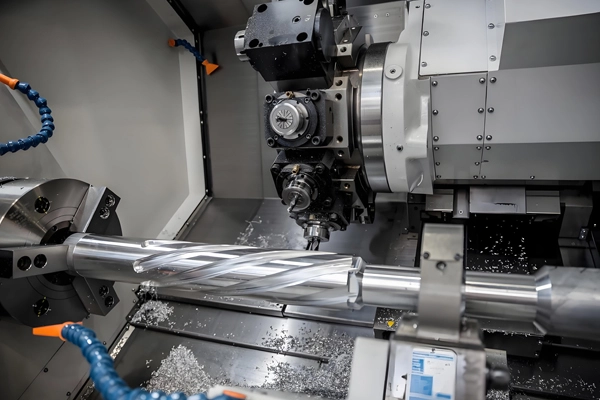
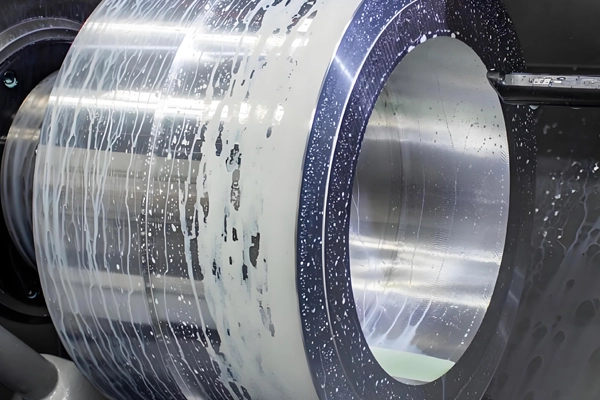
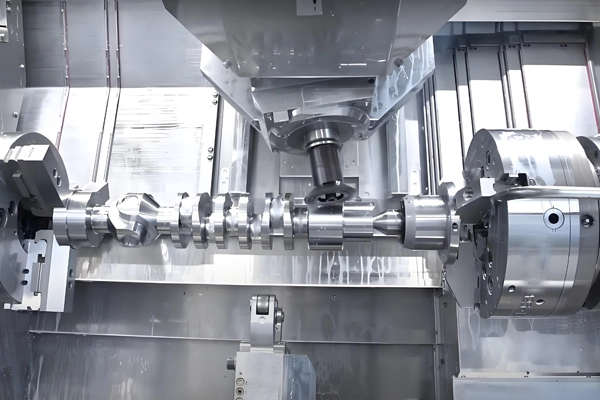
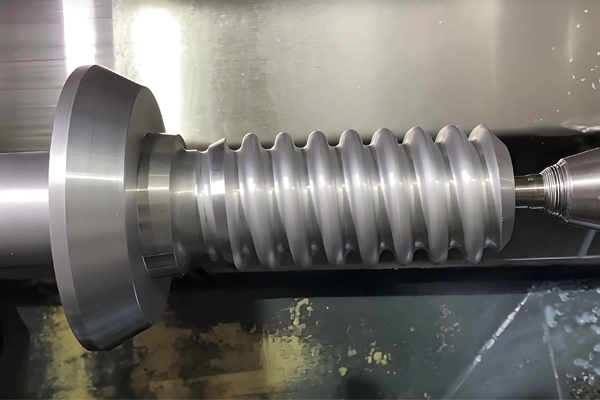
Applications of CNC Milling for Castings and Forgings
1. Precision Machining:
Achieves tight tolerances and intricate geometries on cast and forged parts.
Common in automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial machinery sectors.
2. Surface Finishing:
3. Hole Drilling and Tapping:
4. Contour Milling:
5. Resurfacing and Trimming:
Machines Used for CNC Milling
1. Vertical Machining Centers (VMC):
Ideal for flat or slightly contoured components.
Commonly used for operations like drilling, tapping, and face milling.
2. Horizontal Machining Centers (HMC):
3. 5-Axis CNC Mills:
4. Specialized CNC Lathes with Milling Attachments:
5. High-Speed CNC Mills:
Dimensional Inspection Measures
1. Manual Inspection Tools:
2. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM):
3. Optical Comparators:
4. Laser Scanners and 3D Probes:
5. Surface Roughness Testers:
6. Gauge Blocks and Fixtures:
Inspection Reports
1. First Article Inspection (FAI):
2. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
3. Material Test Reports (MTR):
4. Dimensional Inspection Reports:
5. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Reports:
Quality Control Measures
1. Pre-Machining Quality Checks:
2. In-Process Monitoring:
3. Post-Machining Inspections:
4. Tool Condition Monitoring:
5. Quality Management Systems (QMS):
6. Traceability:
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi