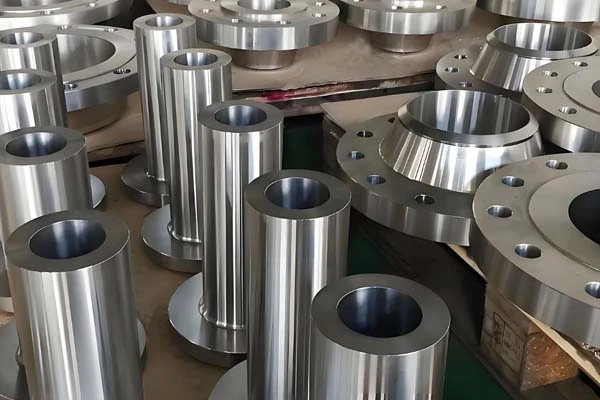
Advantages of Alloy Steel Forgings
Improved Mechanical Properties: Alloying elements enhance the steel's strength, hardness, toughness, and wear resistance.
Fatigue Resistance: Alloy steel forgings provide excellent resistance to fatigue, which is critical for components subjected to cyclic loading.
Ductility and Toughness: These materials maintain ductility and toughness, reducing the risk of brittleness.
Wear Resistance: Many alloy steels are engineered for wear resistance, especially in abrasive environments.
Heat Resistance: Alloy steels can be designed to withstand high temperatures without losing strength, making them ideal for high-heat applications.
Applications of Alloy Steel Forgings
1. Automotive Industry
Crankshafts: Alloy steels, especially those containing chromium and nickel, are used to forge crankshafts. These components require high strength and resistance to cyclic stresses and fatigue.
Transmission Parts: Gears, shafts, and clutch components made from alloy steel are designed for high-load capacity, wear resistance, and durability in automotive transmission systems.
Suspension Components: Alloy steel forgings are used in control arms, steering knuckles, and axle shafts due to their high impact resistance and strength.
Connecting Rods: These components are forged from alloy steel to provide the necessary strength to handle engine combustion forces.
Benefits in Automotive:
High Performance: Alloy steel forgings allow for high-strength, lightweight, and durable components in demanding automotive applications.
Fatigue Resistance: Alloy steel’s fatigue resistance makes it ideal for parts subjected to repetitive stresses.
2. Oil and Gas Industry
Drill Collars and Tooling: Drill collars, drill bits, and other heavy-duty tooling used in drilling operations are often forged from alloy steels to provide high strength and resistance to wear and impact in abrasive, high-pressure environments.
Valve Components: Valve bodies, seats, and fittings used in oil and gas pipelines are forged from alloy steels, which provide resistance to pressure, corrosion, and fatigue.
Flanges and Connectors: Flanges and connectors used in piping systems must withstand high pressure and temperature, making alloy steel forgings ideal due to their toughness and strength.
Benefits in Oil and Gas:
Wear and Corrosion Resistance: Alloy steel forgings are resistant to corrosion and abrasion, crucial for oil and gas applications.
High Strength: Alloy steels provide the strength needed to withstand high-pressure environments and harsh operational conditions.
3. Power Generation
Turbine Parts: Turbine blades, discs, and shafts in power plants are forged from alloy steels to provide high mechanical strength and resistance to fatigue under the extreme conditions present in steam and gas turbines.
Pump Shafts and Impellers: High-strength alloy steel forgings are used for pump shafts, impellers, and other critical components that handle high pressures and corrosive fluids.
Valve Components: Valve bodies and actuators in power generation plants are often made from alloy steel due to its resistance to both high temperatures and corrosion.
Benefits in Power Generation:
Thermal Stability: Alloy steel forgings can handle high thermal stresses without losing mechanical properties.
Long Service Life: These components last longer, reducing the need for maintenance and improving operational efficiency.
4. Mining and Construction
Mining Equipment: Components like drill rods, shovels, bucket teeth, and crusher components are often made from alloy steels due to their durability and ability to withstand extreme wear and high impact.
Heavy Equipment Parts: Axles, gear shafts, bearings, and hydraulic cylinders in heavy-duty construction equipment are forged from alloy steels to handle the heavy loads and continuous operation in mining and construction machinery.
Crawler Tracks: Alloy steel is used for crawler tracks in construction machinery to provide high resistance to wear and impact.
Benefits in Mining and Construction:
Durability: Alloy steel forgings are designed to endure harsh environments and continue functioning under stress.
Wear Resistance: These components resist abrasion, reducing the need for frequent replacements in mining equipment.
5. Marine Industry
Propeller Shafts: Alloy steel forgings are used for propeller shafts in ships, providing the necessary strength to withstand the rotational forces and impact encountered in marine environments.
Turbine and Engine Parts: Turbine components and engine parts in marine propulsion systems are forged from alloy steels for their strength, heat resistance, and fatigue resistance.
Hull Components: Components like keels, rudders, and hatches are often forged from alloy steels for strength and durability in saltwater environments.
Benefits in Marine:
Corrosion Resistance: Alloy steel forgings are resistant to corrosion, which is crucial for marine applications.
Strength and Toughness: These components must withstand harsh marine conditions, including high stress and fatigue.
Common Alloying Elements in Alloy Steel Forgings
1. Chromium (Cr): Enhances hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
2. Nickel (Ni): Improves toughness, strength, and resistance to impact.
3. Molybdenum (Mo): Increases strength, toughness, and resistance to high temperatures.
4. Vanadium (V): Improves strength and resistance to wear and fatigue.
5. Manganese (Mn): Increases strength and hardness, improves ductility.
6. Silicon (Si): Increases strength and helps with heat resistance.
Conclusion
Alloy steel forgings are critical in industries where performance, durability, and strength are paramount. By combining various alloying elements, manufacturers can tailor the properties of the steel to meet the specific needs of each application. Whether in automotive, oil and gas, power generation, or mining, alloy steel forgings provide superior mechanical properties, including improved fatigue resistance, toughness, and wear resistance, ensuring the reliability and longevity of components in even the harshest environments.
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi