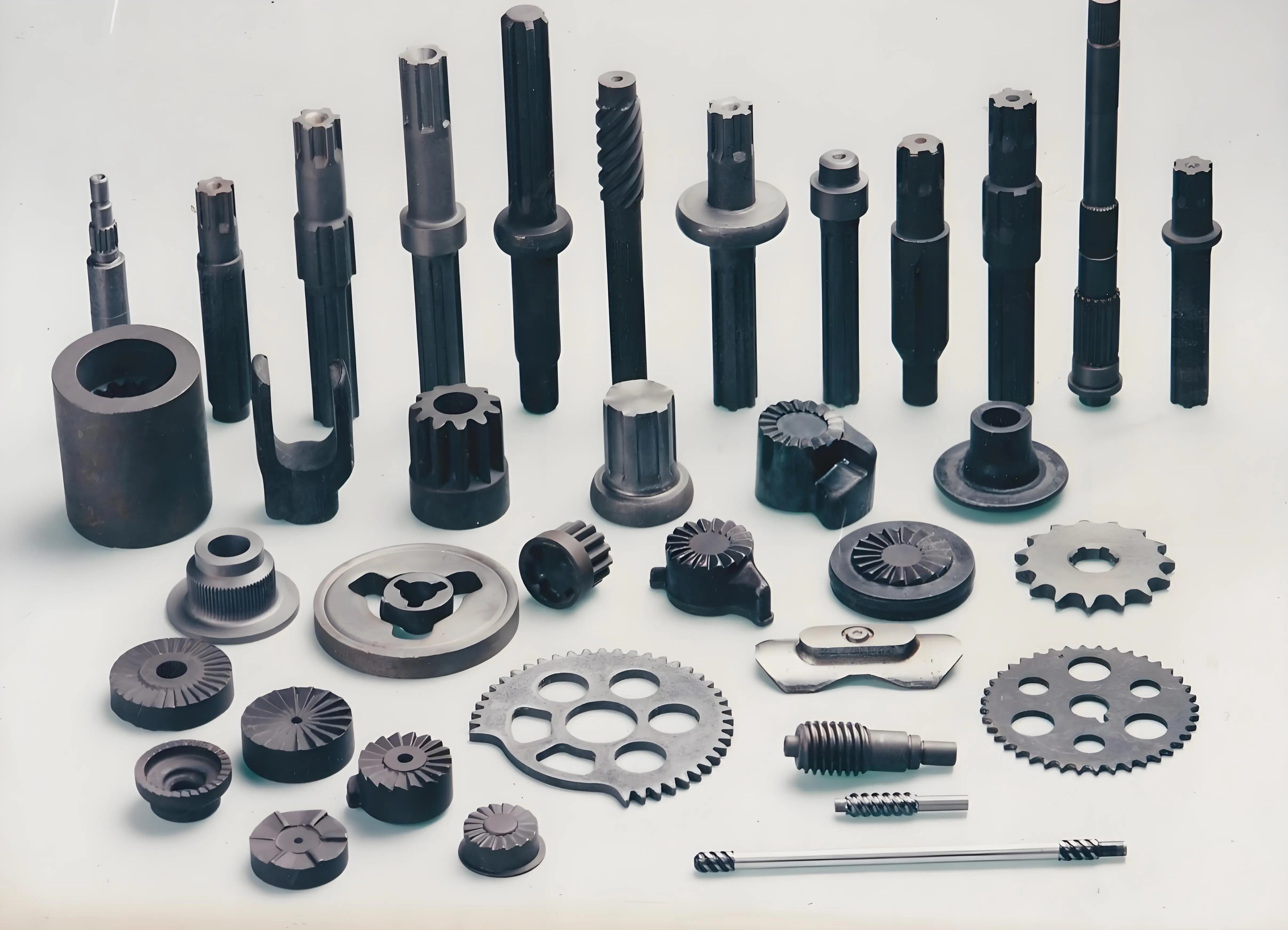
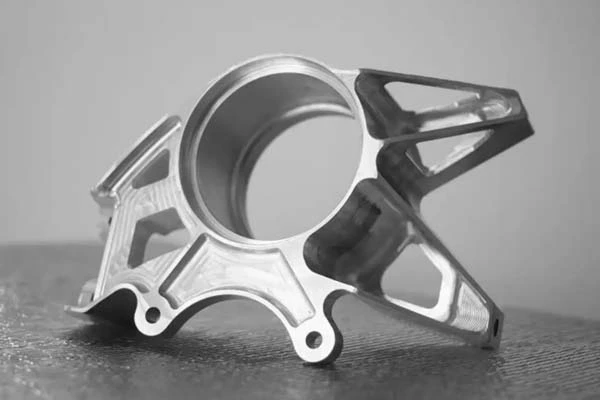
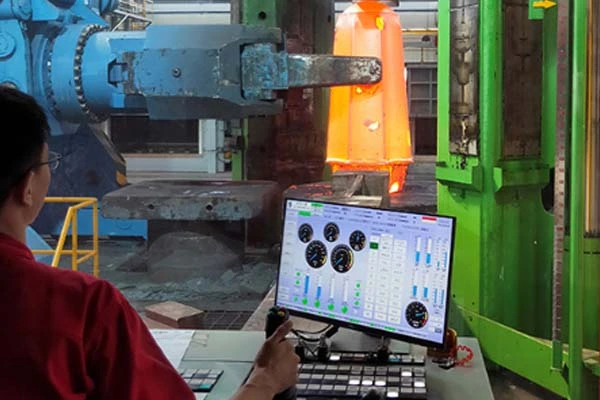
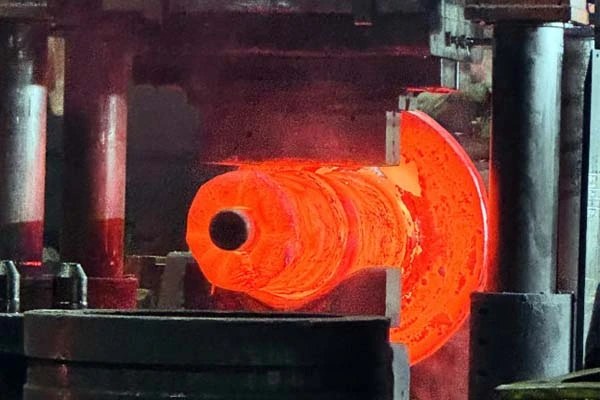
Advantages Of Cold Forging
Cold forging is an environmentally friendly manufacturing process in which the workpiece can be formed at high pressure and low temperature. This cold forging process is able to ensure there are no bubbles, pores or any other impurities in the material, resulting in a very high quality cold forging product.
Compared with other manufacturing methods, the main advantages of cold forging are small dimensional tolerances, good surface finish, and low cost materials that can be worked to obtain the required strength and hardened without heat treatment. If you are searching for a dependable cold forging factory, don't hesitate to contact us to get the latest price!
Application Of Cold Forging
Cold forging is one of the most widely used chip free molding processes and usually does not require machining beyond drilling. The generally accepted cold forging definition is bulk material formed or forged at room temperature without heating the initial slug or intermediate stage.
Cold forging is growing a high popularity in the automotive industry for the manufacture of steering and suspension components, anti-lock braking systems, axles, drill bits, clutch hubs, gears, pinions, pins, steps, and intermediate shafts and sleeves.
Cold Forging Vs Hot Forging
Cold forging process is a molding process carried out at room temperature,which is cold forging temperature. The advantage of cold forging is that we get a good surface finish for the cold forging product.
While during the hot forging process, heat is applied to soften the sheet metal.
The main difference between hot forging and cold forging is that the high temperature of hot forging gives the metal a finer and more complex shape than cold forging.
Cold Forging Process

Cold Forging Materials
Cold forging is the process of plastically deforming a metal material at room temperature while applying massive pressure.
Other key advantages of the cold forming process, in addition to improved overall material properties, include higher dimensional accuracy than forged parts, excellent surface quality, and no need to apply additional energy into the process, such as extreme temperatures.
Cold forging materials that can be cold formed at Walkson include, but are not limited to:
Carbon steels, Alloy steels, Stainless steel, Copper, Aluminum, Bronze, Nickel alloys.
Advantages and Difficulties of Cold Forging Materials
| Advantages | Difficulties |
| Near-net-shape forming | Extensive treatment of the work piece |
| Superior dimensional accuracy when compared to forged parts | Forming degree is lower than with hot forming. |
| Material utilization is extremely high | Complex forms difficult to realize |
| No scaling | Higher tool expenditure |
| High surface quality |
|
| Work piece strength is increased through strain hardening. |
|
| Expedient grain flow as with hot forming |
|
| No heating necessary |
|
Characteristics of Types of Cold Forging Materials 1
| Sr. | Grade | C % | Si % | Mn % | S % Max | P % Max | Cr % | B 7% | Mo % | Pb % | Ni % | Other |
| 1.1 | AISI 1006 | 0.06 Max | 0.10 Max | 0.25-0.40 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.2 | AISI 1008 | 0.10 Max | 0.10 Max | 0.30-0.50 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.3 | AISI 1010 | 0.08-0.13 | 0.10 Max | 0.30-0.60 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.4 | AISI 1015 | 0.13-0.18 | 0.15 Max | 0.30-0.60 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.5 | AISI 1018 | 0.15-0.20 | 0.05-0.10 | 0.60-0.90 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 1.6 | EN 1AL | 0.08-0.15 | 0.10 Max | 0.85-1.15 | 0.26-0.35 | 0.04-0.09 |
|
|
| 0.25-0.35 |
|
|
| 1.7 | EN 1A | 0.07-0.15 | 0.10 Max | 0.80-1.20 | 0.20-0.30 | 0.060 Max |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of Types of Cold Forging Materials 2
| Sr. | Grade | C % | Si % | Mn % | S % Max | P % Max | Cr % | B 7% | Mo % | Pb % | Ni % | Other |
| 3.1 | SCM 415H | 0.12-0.18 | 0.15 -0.35 | 0.55 -0.90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.85-1.25 |
| 0.15 -0.35 |
| 0.25 Max |
|
| 3.2 | SCM 435 | 0.32-0.39 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.55 -0.90 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.80-1.25 |
| 0.15 -0.35 |
| 1.30-1.80 |
|
| 3.3 | AISI 4135 | 0.33-0.38 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.70 -0.90 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 0.15 -0.35 |
| 0.25 Max |
|
| 3.4 | EN 24 | 0.35-0.45 | 0.10 -0.35 | 0.45 -0.70 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.90-1.40 |
| 0.15 -0.35 |
| 1.30-1.80 |
|
| 3.5 | AISI 4140 | 0.38-0.43 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.75 -1.00 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 0.15 -0.25 |
|
|
|
| 3.6 | AISI 4140M | 0.38-0.43 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.75 -0.90 | 0.005 | 0.015 | 0.80-1.10 |
| 0.15 -0.25 |
|
|
|
| 3.7 | AISI 5140 | 0.38-0.43 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.70 -0.90 | 0.04 | 0.035 | 0.70 -0.90 |
|
|
|
|
|
| 3.8 | AISI 1541 | 0.36-0.44 | 0.15 -0.30 | 1.35-1.65 | 0.05 | 0.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of Types of Cold Forging Materials 3
| Sr. | Grade | C % | Si % | Mn % | S % Max | P % Max | Cr % | B % | Mo % | Pb % | Ni % | Other |
| 2.1 | AISI 10821 M | 0.18-0.23 | 0.30 Max | 0.80-1.10 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.10-0.20 | 0.0005-0.003 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.2 | AISI 15B25 | 0.23-0.28 | 0.30 Max | 0.90-1.30 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.10-0.20 | 0.0005-0.003 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.3 | DIN 19MnB4M | 0.20-0.25 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.30-0.40 | 0.0006-0.003 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.4 | AISI 15B41 | 0.38-0.44 | 0.15 -0.30 | 1.35-1.65 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.10-0.20 | 0.0006-0.003 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.5 | AISII 10936M | 0.34-0.39 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.80-1.10 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.20-0.40 | 0.0006-0.003 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.6 | DIN 36CrB4 | 0.34-0.38 | 0.10 Max | 0.60-0.90 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.90-1.20 | 0.0015-0.005 |
|
|
|
|
| 2.7 | AISI 51B35M | 0.34-0.40 | 0.15 -0.30 | 0.35-0.50 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.80-1.15 | 0.0006-0.003 | 0.10 Max |
| 0.15 Max |
|
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi