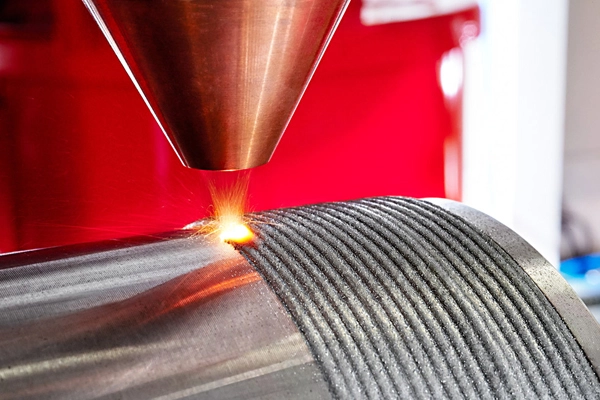
1. Key Applications of Hardfacing in Power Generation
Power generation plants, especially coal-fired and thermal plants, deal with high-temperature conditions, abrasive particulate matter (such as coal, ash, and clinker), and intense mechanical stresses. Hardfacing is essential for protecting critical parts from wear, corrosion, and high-temperature damage.
A. Coal Handling Equipment
Coal handling is a critical process in thermal power plants. It involves the movement, storage, and preparation of coal, and this equipment is exposed to significant wear from abrasive coal dust and impacts from large coal lumps.
· Coal Crushers
Application: Crushers are used to break down large lumps of coal into smaller pieces for combustion in the boiler. Coal crushers face significant abrasive wear from the coal particles as well as impact forces.
Benefits: Hardfacing crusher hammers, rolls, and liners with materials like chromium carbide (CrC) or tungsten carbide (WC) can significantly extend the life of these components by improving their resistance to both impact and abrasion, leading to reduced maintenance and operational costs.
· Coal Pulverizers
Application: Pulverizers grind coal into a fine powder for combustion. The grinding components, including the grinding tables, rolls, and blades, are subjected to extreme wear from the abrasive coal dust.
Benefits: Hardfacing pulverizer components with wear-resistant alloys such as CrC or WC improves their performance by extending service life, reducing downtime, and increasing grinding efficiency.
· Conveyor Systems
Application: Conveyor belts and rollers transport coal throughout the plant. These components are exposed to wear from abrasive coal, dust, and mechanical strain.
Benefits: Hardfacing the conveyor rollers and pulleys with wear-resistant materials enhances their durability, minimizing belt misalignment, reducing friction, and extending component life.
B. Boiler Components
The boiler in a thermal power plant is exposed to high temperatures, pressure, and abrasive particles. Components like superheaters, economizers, and air preheaters must withstand thermal cycling and corrosion, in addition to abrasive wear.
· Superheaters and Reheaters
Application: Superheaters and reheaters are crucial for increasing the temperature of steam used to drive turbines. They are subject to both high temperatures and erosive wear from steam flow and ash particles.
Benefits: Hardfacing with high-temperature-resistant alloys (like cobalt-based or nickel-based alloys) can protect these components from both thermal fatigue and abrasive wear, significantly extending their life.
· Boiler Tubes
Application: Boiler tubes are used to carry steam and water through the furnace, where they are exposed to high heat, pressure, and corrosive gases.
Benefits: Hardfacing the inner surfaces of boiler tubes with alloys that resist oxidation and erosion can help prevent the loss of tube thickness due to abrasive ash and corrosive conditions, reducing the likelihood of tube failures and prolonging the life of the boiler.
C. Steam Turbines and Generators
Steam turbines and generators are the heart of thermal power plants, converting steam energy into mechanical power. These components face wear from mechanical stresses, thermal cycling, and sometimes corrosive steam.
· Turbine Blades
Application: Turbine blades face high-temperature, high-pressure steam and must endure cyclic thermal stresses, erosion, and corrosion.
Benefits: Hardfacing turbine blades with nickel-based alloys or cobalt-based alloys can help prevent erosion, wear, and high-temperature degradation, ensuring smoother operation and longer service life.
· Generator Brushes and Slip Rings
Application: Generator brushes and slip rings are essential for the electrical output of the generator. These components can experience wear due to friction, dust, and operational stresses.
Benefits: Hardfacing the brushes and slip rings with conductive and wear-resistant materials improves their durability, reduces maintenance costs, and helps ensure reliable electrical generation.
D. Ash Handling Equipment
In coal-fired power plants, ash is a byproduct of combustion. Ash handling equipment, such as ash pumps, ash hoppers, and airlocks, can be subject to abrasive wear, especially when handling fly ash.
· Ash Discharge Valves and Hoppers
Application: These components are responsible for managing the discharge of fly ash, which is abrasive and can cause significant wear over time.
Benefits: Hardfacing ash discharge valves and hoppers with wear-resistant materials like chromium carbide or tungsten carbide helps prevent rapid wear, reducing the need for frequent replacement and improving the efficiency of ash handling.
2. Key Applications of Hardfacing in Cement Manufacturing
Cement manufacturing involves high-impact and abrasive environments, with key processes including the grinding of raw materials, clinker production, and the transportation of materials. Hardfacing protects essential components from wear and degradation, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
A. Crushers and Raw Mill Equipment
In cement manufacturing, crushers are used to break down raw materials such as limestone, clay, and gypsum into smaller pieces. Similarly, raw mills grind these materials into fine powder for the cement kiln.
· Crusher Hammers and Rolls
Application: Crushers are used to reduce the size of raw materials before they are sent to the mill. The hammers and rolls experience both impact and abrasive wear.
Benefits: Hardfacing crusher hammers and rolls with abrasion-resistant materials such as tungsten carbide or chromium carbide helps to extend the life of the components and maintain crushing efficiency.
· Raw Mill Liners
Application: Raw mills are used to grind raw materials like limestone, clay, and gypsum into a fine powder. The mill liners are exposed to extreme wear due to the constant grinding action.
Benefits: Hardfacing the raw mill liners with materials such as chromium carbide can significantly increase their wear resistance, reducing the frequency of liner replacements and improving grinding efficiency.
B. Kiln and Preheater Equipment
Cement kilns and preheaters are subjected to extreme temperatures, corrosive gases, and abrasive particles from the combustion process. The equipment used in these areas requires robust protection to maintain operational efficiency.
· Kiln Shells and Tyres
Application: The rotary kiln is used to heat raw materials to high temperatures. The kiln shell and tyres are subjected to thermal stress and abrasive wear from the materials inside.
Benefits: Hardfacing the kiln shell and tyres with high-temperature-resistant alloys protects them from wear and thermal fatigue, helping to maintain the structural integrity of the kiln and extend its operational life.
· Kiln Inlet and Outlet Areas
Application: The inlet and outlet of the cement kiln face extreme heat, abrasiveness from raw feed, and exposure to corrosive gases.
Benefits: Hardfacing these components with high-temperature-resistant coatings can prevent damage from thermal cycling and abrasion, reducing the need for maintenance and extending equipment lifespan.
C. Clinker Cooler and Grate Bar Systems
The clinker cooler is an essential part of cement production, cooling the hot clinker produced in the kiln. The grate bars and other components of the cooler are subjected to high temperatures and abrasive clinker particles.
· Clinker Cooler Grate Bars
Application: The grate bars in the cooler are exposed to abrasive clinker particles and high temperatures, which can cause rapid wear.
Benefits: Hardfacing the grate bars with wear-resistant materials like chromium carbide or tungsten carbide helps protect them from both thermal and abrasive wear, increasing the lifespan of these components and improving cooling efficiency.
D. Cement Mills and Finish Mills
Cement mills are used to grind clinker into cement. These mills experience severe wear due to the grinding of hard clinker particles, which can cause rapid degradation of the grinding media and liners.
· Cement Mill Liners and Diaphragms
Application: Cement mills are exposed to high levels of abrasion and impact from the grinding media and clinker. Mill liners and diaphragms are critical to the grinding process and must be durable to ensure efficient grinding.
Benefits: Hardfacing the cement mill liners and diaphragms with wear-resistant materials helps reduce wear, improve mill efficiency, and extend the life of the equipment.
· Grinding Media (Balls and Rods)
Application: The grinding media inside cement mills undergoes continuous wear from impact and abrasion as they grind clinker and raw materials.
Benefits: Hardfacing the grinding media with high-hardness materials helps increase their lifespan, reducing the frequency of replacement and improving grinding performance.
E. Conveyor Systems and Cement Transport
Conveyor systems are used to transport raw materials, clinker, and finished cement. These systems can experience significant wear from the abrasive nature of the materials being conveyed.
· Conveyor Rollers and Pulleys
Application: Conveyor rollers and pulleys are exposed to wear due to the constant movement of abrasive materials such as clinker and cement.
Benefits: Hardfacing conveyor rollers and pulleys with abrasion-resistant alloys helps reduce wear, maintain smooth operation, and extend the life of the components.
3. Benefits of Hardfacing in Power Generation and Cement Manufacturing
Increased Equipment Longevity: Hardfacing extends the life of critical components exposed to high-impact, high-temperature, and abrasive conditions.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: By increasing component durability, hardfacing reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, leading to significant cost savings.
Minimized Downtime: With hardfaced components, equipment can run for longer periods before maintenance is required, helping to maintain continuous operation and reduce downtime.
Enhanced Efficiency: Hardfacing improves the performance of key equipment, which directly contributes to higher operational efficiency, such as improved grinding or crushing capacity.
Improved Safety: By reducing the likelihood of component failure, hardfacing helps maintain safe and reliable operations, preventing costly and dangerous breakdowns.
Hardfacing is a vital technique for enhancing the durability and performance of machinery in power generation and cement manufacturing. Whether it's improving the efficiency of coal handling equipment, protecting high-temperature boiler components, or extending the life of cement mill liners and kiln parts, hardfacing provides significant benefits. By protecting equipment from wear, impact, and corrosion, hardfacing helps reduce maintenance costs, minimize downtime, and optimize productivity, making it an essential strategy in these industries.
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi