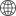
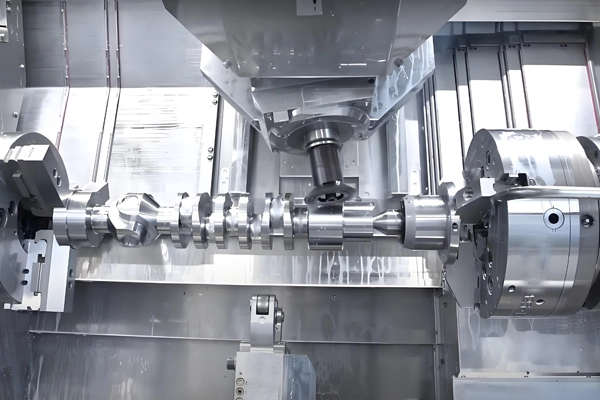
Applications of CNC Drilling and Tapping for Castings and Forgings
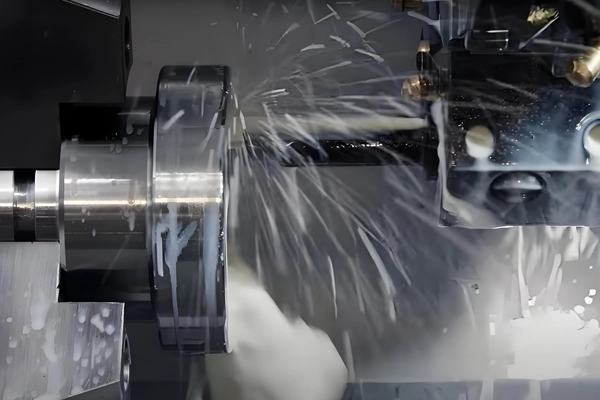
1. Hole Creation:
2. Thread Tapping:
3. Counterboring and Countersinking:
4. Spot Drilling:
5. Specialized Features:
6. High-Volume Production:
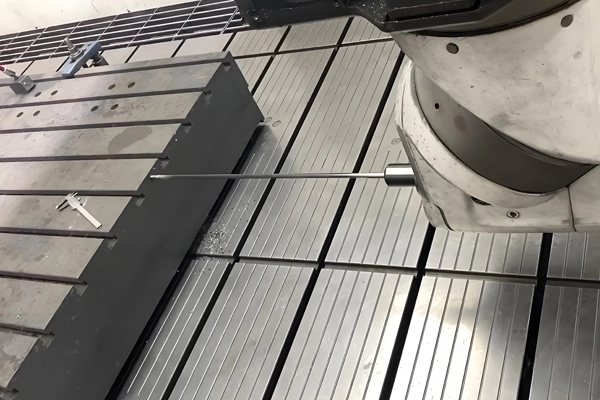
Machines Used for CNC Drilling and Tapping
1. CNC Drilling Machines:
2. CNC Tapping Centers:
3. Vertical and Horizontal Machining Centers:
4. Multi-Spindle CNC Drilling and Tapping Machines:
5. 5-Axis CNC Machines:
6. Radial Drilling Machines:
Dimensional Inspection Measures
1. Plug Gauges and Ring Gauges:
2. Thread Gauges:
3. Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM):
4. Depth Gauges:
5. Optical Comparators:
6. Surface Finish Testers:
7. Bore Scopes:
Inspection Reports
1. First Article Inspection (FAI):
2. Thread Inspection Reports:
3. Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T) Reports:
4. Material Test Reports (MTR):
5. Depth Verification Reports:
6. Dimensional Inspection Reports:
Quality Control Measures
1. Pre-Machining Inspection:
2. Tool Monitoring and Maintenance:
3. In-Process Monitoring:
4. Deburring:
5. Post-Machining Inspection:
6. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
7. Standards Compliance:
8. Traceability:
Advantages of CNC Drilling and Tapping for Castings and Forgings
1. High Precision:
2. Repeatability:
3. Versatility:
4. Efficiency:
5. Cost-Effectiveness:
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi