Copper Sand Casting Process Overview
Copper sand casting follows the same general principles as other sand casting processes but with adjustments to account for the unique properties of copper alloys. The key steps involved in copper sand casting are:
Pattern Creation:
A pattern (usually made from a material like wax, metal, or a thermoplastic material) is designed to replicate the final copper casting. The pattern may be a direct replica of the final product or a negative of it.
In sand casting, the pattern is typically used to create a mold by compacting sand mixed with a binder material around it.
Mold Preparation:
Sand Mold: Sand, usually silica sand, is mixed with a binder like clay or resin to form a mold. For copper, the sand mixture must be designed to withstand the high temperatures of molten copper (typically 1,080°C to 1,150°C).
The mold is created by packing sand around the pattern and then hardening it to form the mold cavity.
Melting Copper:
Copper or copper alloys (such as bronze or brass) are melted in a furnace at high temperatures. Copper has a relatively high melting point (about 1,085°C or 1,984°F), so high-efficiency furnaces are necessary.
The molten copper is then poured into the mold cavity.
Pouring:
The molten copper is carefully poured into the mold through a gating system, which allows it to flow into the mold cavity while minimizing air pockets and defects.
A steady pour is essential to avoid thermal stresses or unwanted cooling rates.
Cooling and Solidification:
Mold Removal and Cleaning:
After the casting has solidified and cooled, the sand mold is broken away to reveal the casting. Any sand or mold material left on the surface is cleaned off, and the casting may undergo additional processes like grinding, sanding, or shot blasting to remove rough spots or sharp edges.
Post-Processing:
The casting may undergo secondary machining, polishing, heat treatment, or coating depending on the specific application.
Heat treatment can be used to improve the mechanical properties of the copper casting, such as its strength and hardness.
Polishing or finishing may be required for aesthetic purposes or to meet specific surface quality standards, especially for decorative items.
Detailed Applications of Copper Sand Casting
Copper sand casting is used to produce parts for a wide range of industries, including electrical, marine, automotive, plumbing, and decorative applications. Copper's desirable properties—such as high electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and strength—make it an ideal material for various professional applications.
1. Oil & Gas and HVAC
Fittings and Valves:
Copper alloys are commonly used for plumbing components such as fittings, pipes, and valves, which need to withstand corrosion and maintain structural integrity in water systems.
Applications: Common in plumbing systems, including water heaters, boilers, and faucets, where copper’s resistance to corrosion is highly valuable.
Heat Exchangers:
Copper’s excellent thermal conductivity makes it ideal for heat exchangers, which are used in HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and industrial cooling applications.
Applications: Used in the production of heat exchanger plates, condenser tubes, and other components involved in heat transfer.
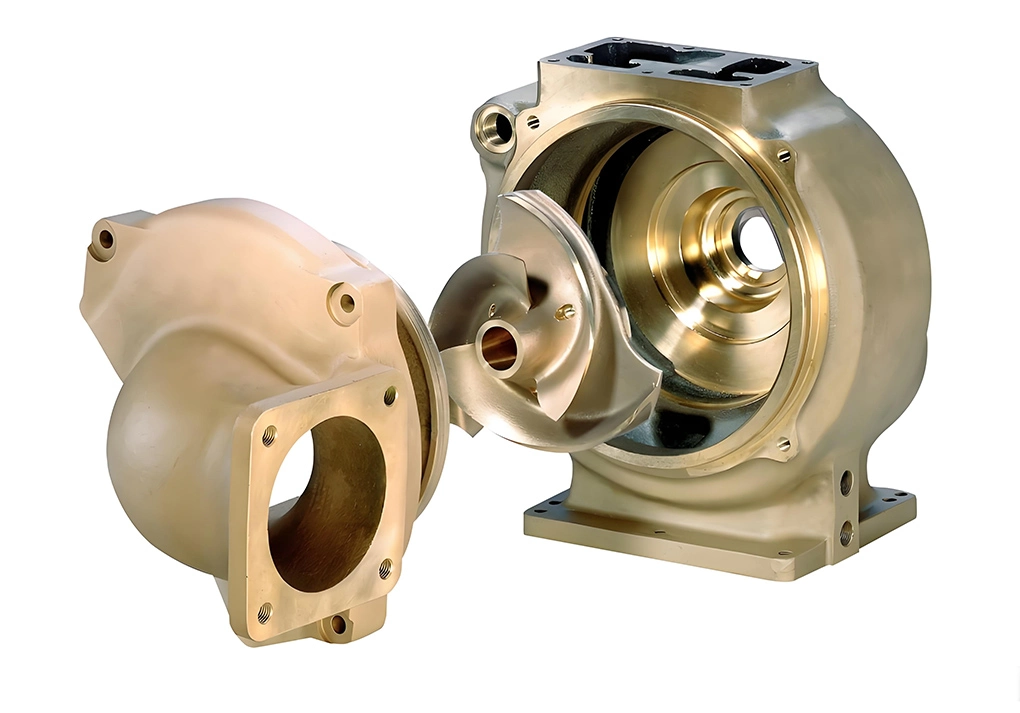
Pumps:
Copper is used to make pump parts such as pump housings, impellers, and other components exposed to fluids. Copper’s resistance to corrosion and biofouling is advantageous for pumps used in water systems, including swimming pools and water treatment plants.
Applications: Used in industrial pumps, circulators, and cooling systems in HVAC and plumbing.
2. Electrical Industry
3. Marine Industry
4. Automotive Industry
5. Industrial Equipment and Machinery
Bearings and Bushings:
Copper alloys like bronze are commonly used for bearings and bushings due to their self-lubricating properties and high wear resistance. Copper-based materials offer low friction and are ideal for moving parts in machinery.
Applications: Used in pumps, motors, and heavy machinery parts to reduce wear and extend service life.
Gears and Gearboxes:
Copper alloys are used in gear manufacturing, particularly for gears that operate in high-temperature and high-stress environments. The alloys’ combination of strength and resistance to wear makes them suitable for this application.
Applications: In industrial machines, motor drives, and automotive gear systems.
6. Decorative and Artistic Applications
7. Industrial and Heavy-Duty Equipment
Conclusion
Copper sand casting is a widely used and highly versatile method for producing copper and copper alloy components in a range of industries. The key benefits of copper—such as its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and strength—make it a material of choice for various applications, from electrical and plumbing systems to marine, automotive, industrial, and decorative components. Sand casting offers flexibility in producing both large and intricate copper components, making it a crucial process for manufacturing high-quality, durable products across many sectors.
 English
English  Deutsch
Deutsch  français
français  русский
русский  فارسی
فارسی  العربية
العربية  Español
Español  日本語
日本語  한국어
한국어  italiano
italiano  português
português  dansk
dansk  Suomi
Suomi